Portable Handheld Device for Glaucoma Screening and Diagnosis
KEY INFORMATION
Healthcare - Medical Devices
TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW
Glaucoma stands as the leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide after cataract. It is expected to affect 111.8 million people by 2040 [1], exacerbates by the aging population globally. Despite its prevalence, 50% of people with glaucoma are undiagnosed. Current methods of imaging the iridocorneal angle for glaucoma diagnosis are severely limited by cost and utility, with traditional gonioscopy being the main method. Gonioscopy is a subjective procedure and the method causes discomfort in patients.
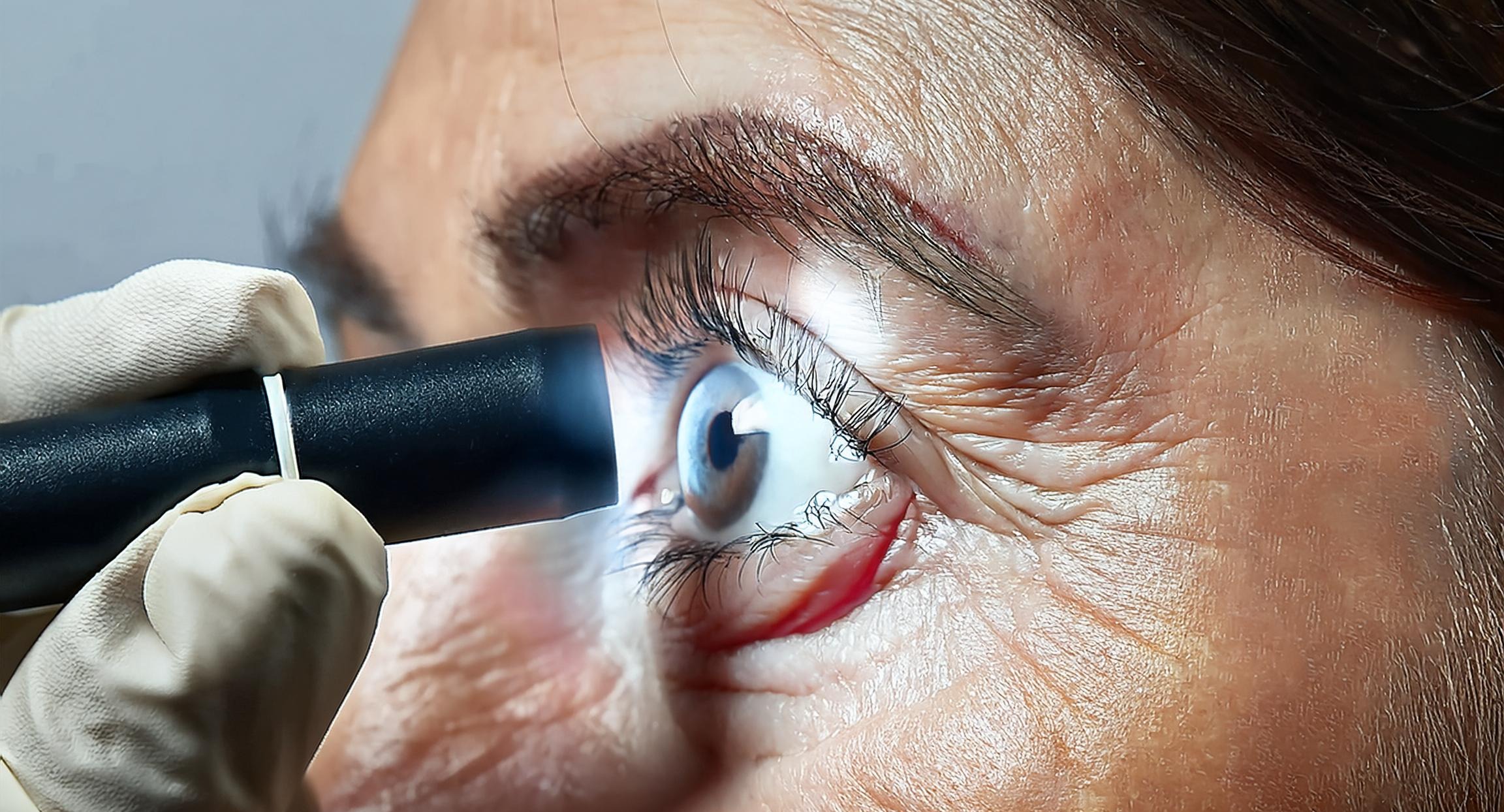
This technology is a compact, handheld device specifically designed to enhance the accessibility of glaucoma diagnosis. With its portable and user-friendly design, it enables the evaluation and automated diagnosis of glaucoma angle, making it suitable for use by non-specialists. The device is complemented by advanced image processing and management software, which facilitates precise and automated angle evaluation, ensuring accurate and efficient diagnostics.
The technology owner seeks collaboration with partners interested in development and licensing opportunities. Medical device manufacturers, technology firms, or individuals passionate about advancing innovative healthcare solutions are invited to collaborate or license the technology. Partnerships can focus on optimizing the design, scaling production, and facilitating successful market entry.
[1] Tham, Y., Li, X., Wong, T. Y., Quigley, H. A., Aung, T., & Cheng, C. (2014). Global Prevalence of Glaucoma and Projections of Glaucoma Burden through 2040. Ophthalmology, 121(11), 2081–2090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.05.013
TECHNOLOGY FEATURES & SPECIFICATIONS
The technology seeks to address critical challenges in glaucoma diagnostics.
- Device Design: Compact, lightweight handheld device, engineered for portability and ease of use.
- Patented Imaging Device: Eye imaging probe with a charge-coupled device camera. This allows the device to image the iridocorneal angle region inside the eyes which is normally obstructed from direct view.
- Automated Diagnosis: Software algorithm for automated diagnosis of glaucoma (development in progress).
POTENTIAL APPLICATIONS
- Primary care as a Screening Device: The technology can be integrated into primary care settings as a quick and reliable screening tool, enabling early detection of glaucoma at the community level. This makes it especially valuable for preventive care initiatives.
- Hospitals use by a Non-Specialist: Hospitals can deploy the device to expand their glaucoma screening capabilities. Its user-friendly design allows non-specialists, such as general practitioners or trained technicians, to conduct evaluations, increasing throughput and accessibility.
- Replacement for Traditional Gonioscopy During Surgery: The device has potential use in surgical settings, serving as a substitute for traditional gonioscopy. Its automated and precise imaging capabilities can streamline intraoperative assessments, enhancing efficiency and outcomes during eye surgeries.
Unique Value Proposition
The technology addresses key limitations of traditional methods, significantly enhancing the accessibility of glaucoma diagnosis while reducing reliance on highly trained specialists. Conventional approaches, such as gonioscopy, require specialized expertise and costly equipment, making them impractical in resource-constrained settings.
By enabling non-specialists and community health workers to perform accurate screenings, this portable and automated solution democratizes eye care, expanding access to underserved populations, including those in rural areas. Additionally, the technology increases productivity by scaling up screening efforts, facilitating broader early detection and diagnosis. These advancements collectively transform glaucoma diagnostics into a more inclusive and efficient process.